Keras float32 model to tflite float16
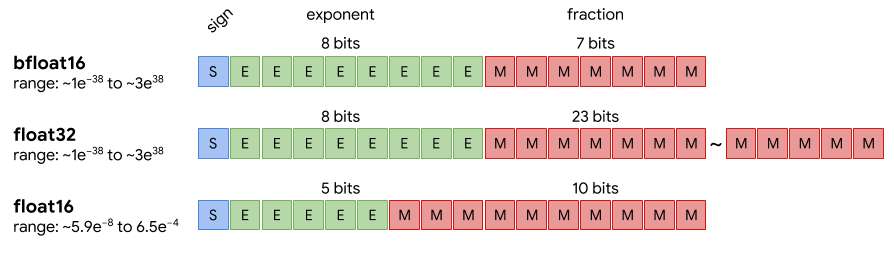 Fig.1 float type에 따른 메모리 구조 비교 예시 (https://medium.com/@fanzongshaoxing/post-training-quantization-of-tensorflow-model-to-fp16-8d66b9dfa77f)
Fig.1 float type에 따른 메모리 구조 비교 예시 (https://medium.com/@fanzongshaoxing/post-training-quantization-of-tensorflow-model-to-fp16-8d66b9dfa77f)
Fig.1 에서도 확인할 수 있듯이 float type을 바꾸면 메모리를 덜 사용할 수 있다는 장점이 있어서, edge device deploy를 가정한 detection 모델의 weight 타입을 변환하는 실험을 진행하였다. tflite로 모델 변환을 하기 위해서 모델을 converter로 load 해야하며, 다양한 방법이 존재하지만 몇몇 방법에서 오류가 발생하여 frozen graph를 불러오는 방법을 선택하였다. 참고로 tflite는 embedded 환경에 최적화된 tool이기 때문에 desktop 환경에서 float 변환을 사용하려는 목적이라면 다른 방법을 찾는 것이 좋겠다.
import tensorflow as tf
converter = tf.compat.v1.lite.TFLiteConverter.from_frozen_graph(
graph_def_file='model.pb',
# both `.pb` and `.pbtxt` files are accepted.
input_arrays=['input'],
input_shapes={'input' : [1, imgsize[0], imgsize[1], num_ch]},
output_arrays=['box_regression',
'classification']
converter.experimental_new_converter=True
converter.target_spec.supported_ops = [tf.lite.OpsSet.TFLITE_BUILTINS,
tf.lite.OpsSet.SELECT_TF_OPS]
tflite_models_dir = pathlib.Path("tflite_retinanet/")
tflite_models_dir.mkdir(exist_ok=True, parents=True)
# for fp32
tflite_fp32_model = converter.convert()
tflite_model_fp32_file = tflite_models_dir/"quant_fp32.tflite"
tflite_model_fp32_file.write_bytes(tflite_fp32_model)
# for fp16
converter.optimizations = [tf.lite.Optimize.DEFAULT]
converter.target_spec.supported_types = [tf.float16]
tflite_fp16_model = converter.convert()
tflite_model_fp16_file = tflite_models_dir/"quant_fp16.tflite"
tflite_model_fp16_file.write_bytes(tflite_fp16_model)
Troubleshooting
확인해봐야겠지만 tutorial 코드에 아래 두 옵션을 추가하니 안돌아가던 것이 돌아간다. (위의 코드는 이를 반영한 버전)
이것이 converter.experimental_new_converter=True를 활성화시켜서인지 아닌지는 확인할 필요가 있음. converter.target_spec.supported_ops 의 효과로 판명났다. converter.experimental_new_converter=True 는 default로 설정되어 있는 것이 아닐까 싶음. 없어도 돌아가긴 하지만 혹시 모르니 넣어보자.
- 이와 관련하여 converter.experimental_new_converter=False 로 설정하면 오류가 발생하는 것을 확인할 수 있음. 이는 예전 버전의 converter를 사용하면서 지원하는 ops의 수가 현저히 줄어들었기 때문으로 생각할 수 있다.
- converter.target_spec.supported_ops을 사용하기 위해서는 converter.experimental_new_converter가 True로 설정되어 있어야 한다.
converter.experimental_new_converter=True converter.target_spec.supported_ops = [tf.lite.OpsSet.TFLITE_BUILTINS, tf.lite.OpsSet.SELECT_TF_OPS]
아래는 tflite 개발자(?)가 올린 New experimental TFLite converter 옵션을 사용하는 이유
Why you should use the new converter
- Enables conversion of new classes of models, including Mask R-CNN, Mobile BERT, and many more
- Adds support for functional control flow (enabled by default in TensorFlow 2.x)
- Tracks original TensorFlow node name and Python code, and exposes them during conversion if errors occur
- Leverages MLIR, Google’s cutting edge compiler technology for ML, which makes it easier to extend to accommodate feature requests
- All existing functionality is supported
Equivalence check를 하기 위해서 tflite로 저장된 모델을 interpreter로 불러왔는데, invoke() (tflite 모델의 inference 명령어이다.) 에서 아래와 같은 메세지와 함께 fail이 발생한다. 원인은 convert 하려는 모델에서 사용한 post processing layer의 TensorArrayScatterV3가 아직 tflite에서 지원되지 않기 때문이이다.
- 이를 해결하기 위해 임시방편으로 모델 conversion을 post processing layer 이전까지만 하고 이후의 과정은 별도로 구현하는 방법을 선택하였다.
Float conversion 효과 확인
Byte check
71M quant_fp16.tflite
141M quant_fp32.tflite
Equivalence check
| Image No. | rmse(bbox) | rmse(softmax score) | rmse(argmax(softmax score)) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Img 1 | 0.210210204 | 0.000126329 | 0.000166415 |
| Img 2 | 0.209912494 | 0.000155861 | 0.000202240 |
| Img 3 | 0.208083674 | 0.000117018 | 0.000152367 |
| Img 4 | 0.209897473 | 0.000105126 | 0.000138428 |
Conclusion
- 위 실험 결과를 보면 float32 모델과 float16 모델의 용량 차이는 절반이나 나는데, prediction 수치는 거의 차이가 없음을 확인할 수 있다.
- 따라서, 모델을 deploy하는 환경이 저사양의 edge 환경이라면, float32->float16 conversion까지 진행해주는 것이 당연한 수순이라고 생각할 수 있겠다.
Comments